Detailed explanation of 6-minute walking test (6MWT) for cardiopulmonary rehabilitation
Want to know your cardiopulmonary function? Then quickly find a flat and accessible corridor (25-30 meters) and walk for six minutes. Dare you walk for six minutes?
.gif)
What Is the Six-Minute Walk Test?
Six minute walk test is a fixed time field test widely used in various rehabilitation interventions. It is an effective tool to analyze the functional ability of patients with cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases. Functional ability is the ability of subjects to carry out daily activities or activities of daily living (such as bathing, dressing or walking). The 6-minute walk test is a sub maximum exercise test to assess aerobic capacity and endurance.
.jpg)
The six minute walk test is used as an alternative to the cardiopulmonary exercise test (COET) because it is cost-effective, easy to perform, and can be evaluated by walking distance within six minutes at a self selected speed. 6MWT was developed by the American Thoracic Association. It was officially launched in 2002 with a comprehensive guide. At present, the six minute walk test (6MWT) has been well standardized by the American Thoracic Association/European Respiratory Society (ATS/ERS), and is the most commonly used test in clinical practice to determine the functional capacity of patients with chronic lung disease.
Origin of 6MWT


In the early 1960s, Balke put forward a simple method to evaluate the functional compensation ability, that is, to measure the walking distance within a specified time. Then a 12 minute field walking test was developed to measure the fitness of healthy people. However, it was difficult for patients with respiratory diseases to walk for 12 minutes. Later, it was found that the effect of 6 minute walking was the same as that of 12 minute walking.
.png)
In 1985, Guyatt and others took the lead in applying the 6-minute walking test (6MWT) to evaluate the activity of patients with heart failure. According to the American Thoracic Society (ATS) Six minute Walk Test Guide, 6MWT needs to measure the maximum distance of patients' 6-minute walk in a flat and barrier free corridor, and the speed is controlled by the patients themselves. This test method is simple, easy and safe, and can be completed only by a 100 foot (about 30M) corridor and some simple monitoring equipment (such as timers, chairs for patients to rest, and other emergency drugs).

As most activities of patients in daily life need to be completed at the level of submaximal exercise, as a submaximal exercise test, 6MWT can better reproduce the daily physiological state of patients and reflect the cardiac function of patients under physiological state. It is a non-invasive, simple, safe, easy to manage, and well tolerated clinical test, which has been widely used in recent years.
The American Thoracic Society describes the 6-minute walk test as a measure of functional status or health. It is used as a simple measure of aerobic exercise capacity. The results of this test may allow your doctor to make a simpler measurement of your cardiopulmonary function. This test can be used to monitor the treatment response of your heart, lungs and other health problems. Now this test is usually used for patients with pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary interstitial disease, lung transplantation pre evaluation or COPD disease.

Clinical indications

Intended Population
6MWT can be used for preschool children (2-5 years old), children (6-12 years old), adults (18-64 years old), and the elderly (over 65 years old), with a wide diagnostic range. The test was originally designed to help assess patients with heart and lung problems. Gradually, it has been introduced into many other situations.It assesses the individual's functional ability and provides valuable information about all systems in physical activity, including the lung and cardiovascular system, blood circulation, neuromuscular units, body metabolism and peripheral circulation. The results can be used to evaluate the treatment results, exercise tolerance and determine the prognosis of patients

6MWT clinical use conditions
According to the guidelines of American Thoracic Association, the indications of 6MWT are:
1. Comparison before and after treatment
Lung transplantation;
Lung surgery (including pneumonectomy and lung volume reduction);
Lung rehabilitation;
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
Pulmonary hypertension;
Cardiac insufficiency.
2. Functional ability and sports endurance evaluation
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
Cystic fibrosis;
Incomplete mental skills;
Peripheral vascular disease;
Fibromyalgia;
Elderly patients.
3. Prediction of incidence rate and mortality
Incomplete mental skills;
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
Pulmonary hypertension.

Contraindications to the six minute walk test


Absolute contraindication of 6MWT
: Including unstable angina or myocardial infarction, worsening heart failure, acute deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary embolism, myocarditis or endocarditis within 1 month.Relative contraindications include:
The resting heart rate exceeds 120 times/minute, the systolic pressure exceeds 180mmHg, the diastolic pressure exceeds 100mmHg, and uncontrolled arterial hypertension.
Patients with any of the above conditions should inform the physician applying for or guiding the examination, so that they can make clinical evaluation and decide whether to conduct the examination.6
ECG results within months should also be reviewed before examination.Stable exertional angina is not an absolute contraindication of 6MWT, but patients should be tested after using angina drugs, and should be prepared with first-aid nitrates.
Six minute walk test procedure
Required equipment:
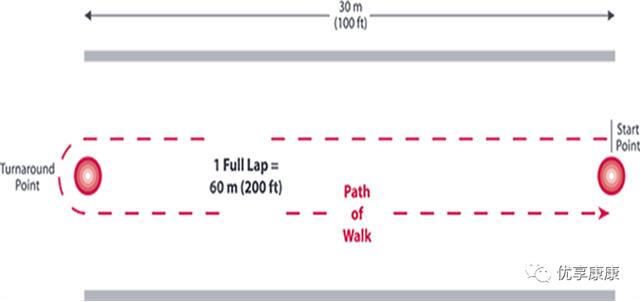
·A straight and flat road 30 meters long;
·Tape measure/measuring rule;
·Two cones are used to mark the starting point and turning point;
·Stopwatch/timer;
·Mechanical counter;
·Easy to move chair;
·Blood pressure meter;
·Pulse oximeter;
·Borg scale (for dyspnea score);
·Oxygen;
·Cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment.

Preparation of path/location:
·The path for 6MWT shall be 30m long, straight and uninterrupted;
·In order to facilitate measurement, marks must be made every 3 meters;
·Two cones must be placed at the starting point and turning point;
·One chair should be placed in the middle, or two chairs can be placed at the starting point and turning point, so that patients can rest during or after the test;
·Ensure easy access to oxygen and telephone in case of emergency.
Preparation of patients:
·Ensure that the patient wears comfortable clothes and shoes;
·If the patient is a regular user of any walker, instructions for using the walker must be given during the test
·Any prescription drugs (such as bronchodilators) should be taken before the test;
·If the patient is replenishing oxygen, use a portable oxygen bottle with the same oxygen level as he/she usually uses;
·Eat some light food before the morning and afternoon test;
·The patient should rest for at least 10 minutes before the test and should not take any strenuous exercise.
Six minute walk test
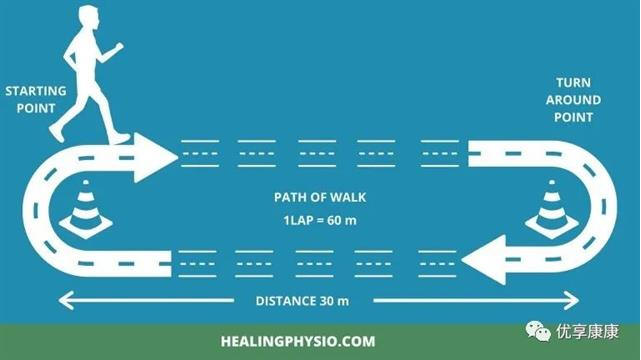
Six minute walk test chart
·Ensure that the medical history and contraindications are reassessed;
·Record vital signs - blood pressure, heart rate, blood oxygen saturation (blood oxygen saturation), and ensure patient stability;
·Ask the patient to stand up and assess his/her dyspnea and fatigue with the Borg scale;
·Set the lap speed counter to zero and move it to the starting point;
·Patient guidance and encouragement must be standardized (according to ATS);
·Instruct the patient as follows: "The purpose of this test is to walk for as long as possible for 6 minutes. You will walk back and forth in this corridor. Six minutes is a long walk time, so you will work hard. You may be out of breath or exhausted. If necessary, you can slow down, stop and rest. You can lean against the wall when resting, but you should resume walking as soon as possible. You will walk around the cone. You should rotate around the cone briskly, without hesitation Continue to return in the other direction. Now I want to show you. Please do not hesitate to watch me turn around. Demonstrate by walking and instruct the patient to walk as much as possible within 6 minutes, not to run or jog. Clarify any questions from the patient.
·Put yourself and the patient at the starting point. Once the patient starts walking, start the timer;
·When you accompany the patient, you must walk behind him/her to avoid affecting the patient's walking speed;

Use the following standard incentives:
·After the first minute, "You did well. You have 5 minutes left".
·With four minutes left, "Keep working hard. You have four minutes left.".
·When there are 3 minutes left, "You are doing well. You are half done".
·When there are 2 minutes left, "Keep working hard. You only have 2 minutes left".
·When there is 1 minute left, "You are doing well. You have only 1 minute left".
·When the timer is finished with 15 seconds left, "I will tell you to stop later. When I do this, stop where you are, and I will come to you.".
·6 minutes, "please stay where you are".
·Once stopped, place a mark at the distance from the stop so that the patient can sit comfortably. If the patient likes to stand, let him/her stand.
·Immediately record the post vital signs - blood pressure, heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, and use the Borg scale to assess the speed of perceived exertion.
·Heart rate recovery (HRR) of 3 minutes per minute can be recorded to evaluate any abnormal HRR related to incidence rate and mortality of various respiratory diseases. [Note: This step is an exception]
·If the patient stops to rest during the test, keep the timer running.
·If the patient stops the test, be sure to ask why he/she stopped the test or what restricted him/her from stopping the test.
·Record the total number of turns. The extra walking distance can be measured with a tape measure, accurate to the marked meters.
·Congratulate the patient on their efforts and monitor for any signs and symptoms.
Minute walk test formula
This formula is used to predict the normal value of the six minute walk test
Predicted 6MWD=218+[5.14 x height cm – 5.32 x age] – [1.80 x weight kg]+[51.31 x gender]The gender factor is included in the equation: male=1, female=0
For example, a 65 year old male patient with a height of 159cm and a weight of 38kg completed 5 laps in the six minute walk test.
Calculate the normal value of the distance he should walk:
6MWD=218+[5.14 x height cm – 5.32 x age] – [1.80 x weight kg]+[51.31 x gender]
= 218+[5.14 x 159–5.32 x 65]–[1.80 x 38]+[51.31 x 1]
= 218+[471.46]–68.4+51.31
=672.37m
Therefore, the predicted normal value of 6MWT is 672.37m. But the patient completed five laps, or 300 meters
explain
According to the study, the walking distance of healthy subjects in the six minute walking test ranged from 400 meters to 700 meters. The reference values of the average distance of a group of healthy men and a group of healthy women were 735 meters (98 meters) to 580 meters and 657 meters (56 meters) to 500 meters, respectively. If the distance of walking in 6MWT is close to the normal predicted value, it indicates that the functional capacity is good. Adding more than 60 meters in subsequent tests is considered to be a significant improvement in rehabilitation results. However, 6MWT also has many other influencing factors, such as the experience of the testee, the communication between the testee and the testee, and the understanding of the testee. It is very important to unlock the test to the patient before the test starts!

.gif)
.jpg)


.png)












