What is the grading standard for the total distance of 6-minute walk? What does 6 minute change represent?

The 6-minute walk test (6MWT) is one of the most common submaximal exercise tests. It was developed by Bakle in the 1960s for the evaluation of physical fitness. The functional state and reserves of the body are evaluated by measuring the distance traveled within a specified time. The results of 6MWT have two functions: one is to judge the cardiopulmonary function mainly by the absolute value of 6MWD or the percentage of the absolute value in the predicted value; The second is to judge the improvement/deterioration of functions through the changes of 6MWD before and after.
Absolute value of 6MWD or percentage of absolute value to estimated value
There are many factors influencing the predicted value of 6MWD, and there is no consensus at present. Although there are many factors that affect 6MWD, the absolute value of walking distance provides useful information. For example, in patients with COPD, 6MWD is used to calculate the BODE index, which defines the prognosis of the disease. The cut-off values of 6 MWD for functional damage severity stratification are 350m, 250m and 150m. Among patients with COPD, absolute 6MWD is an important predictor of mortality, and patients with a distance of more than 400 meters have the lowest risk. Early studies in patients eligible for pneumonectomy reported thresholds of 300m and 450m − 500m to predict postoperative complications. For the prediction of 6MWD, the Chinese expert consensus on the clinical application of 6-minute walk test in elderly patients suggests that:
Male: 6MWD (m)=233.205+[4.31 × Height (cm)] - (4.01 × Age+6.14 × BMI);
Female: 6MWD (m)=285.011+[1.041 × Height (cm)] - (0.678 × Age+2.189 × BMI)。
In addition, the calculation method of 6MWD prediction value is also given in some foreign studies (see the figure below).
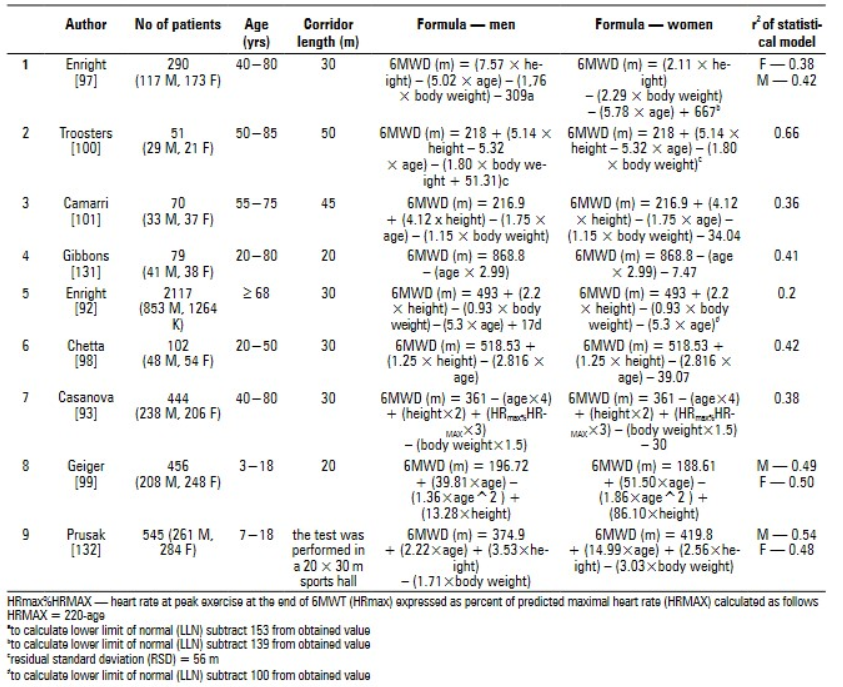
1. Application of 6MWD in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PAH)
In patients with idiopathic pulmonary hypertension, the critical value of 6MWD for predicting survival was 332m. According to experts from the American College of Cardiology, the increase of 6MWD to ≥ 380 − 440M should be one of the goals of the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary hypertension.
2. Application of 6MWD in patients with heart failure (HF)
The Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure (2018 Edition) recommends that 6MWD be used to assess and grade the exercise tolerance of patients with heart failure. 6MWD<150m is severe, 150-450m is moderate, and>450m is mild. Compared with patients with 6MWD>300m, patients with 6MWD<300m had significantly higher mortality (10% vs 3%). The death risk of patients with 6MWD<300m, 300~450m and>450m was also significantly different.
3.Application of 36 MWD in patients with idiopathic fibrosis (IPF)
(Lederer DJ, 2006) et al. showed that in patients with IPF, the mortality of patients with 6MWD<207m was 4 times higher than that of patients with 6MWD>207m. Another study showed that the critical value of 6MWD was 350m, which defined the functional impairment of IPF patients and had a significant impact on mortality risk.
4 Application of 6MWD in elderly patients
In the consensus of Chinese experts on the clinical application of 6-minute walk test for elderly patients (2020 version). According to the evaluation of 6MWT cardiopulmonary function or exercise endurance of the elderly, it is recommended that 6MWD<150m is severe, 150-300m is moderate, 301-450m is mild, and>450m is normal.
5 Percentage of absolute value in estimated value
(Troosters T, 1999) proposed that 6MWD lower than 82% of the predicted value should be regarded as abnormal. The remaining standard deviation formula is as follows. SR=(Actual - Predicted)/RSD

Change value of 6MWD related to improvement/deterioration of prompt function
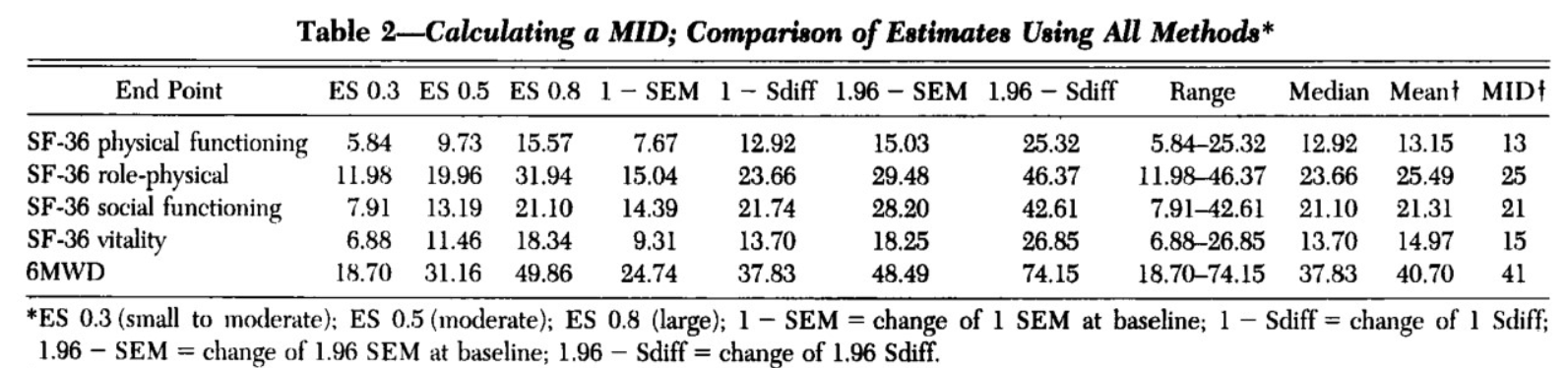
When analyzing the impact of medical intervention, the minimum clinically significant difference (MCID) should be considered to describe 6MWD. The minimum significant change, that is, the minimum change of 6MWD twice before and after treatment, represents the improvement/deterioration of the patient's function.
(Redelmeier DA, 1997) reviewed 77 articles and provided 248 results of different studies on patients with COPD. The threshold value of 54 meters difference in 6-minute walking distance before and after was adopted. In another ECLIPSE study (Polkey MI, 2013), a reduction of 6MWD of>30m within 12 months was associated with a higher risk of mortality (hazard ratio 1.93).
1 MCID of chronic pulmonary disease·
An ERS/ATS system review (Singh SJ, 2014) showed that the MCID of 6MWD in adults with chronic respiratory diseases was 25~33m (1~10 days repeated test).
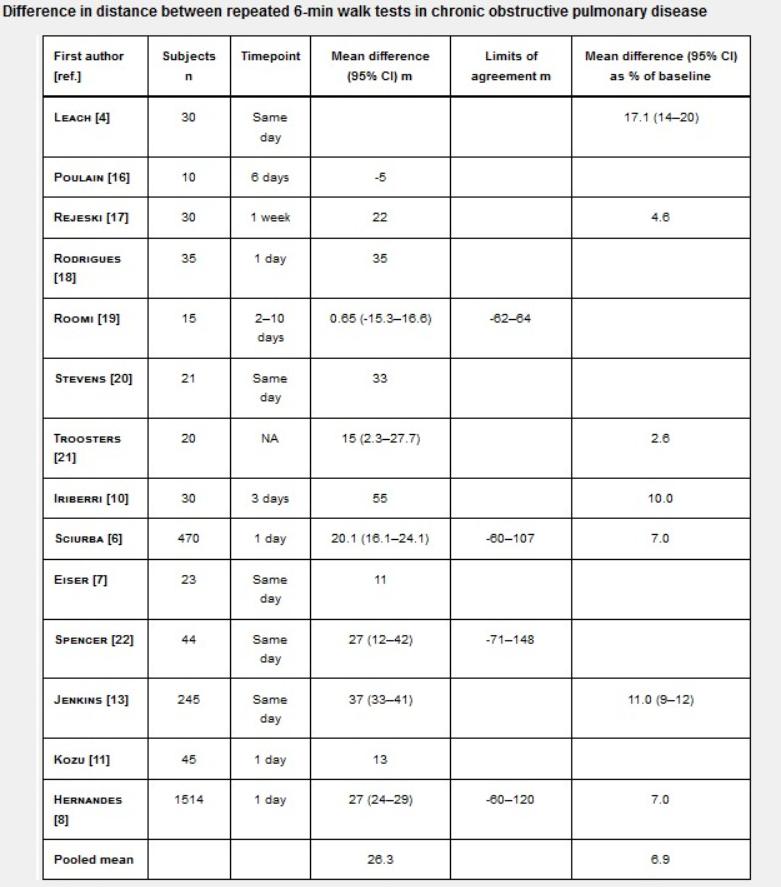
2 MCID of patients with heart failure
In elderly patients with heart failure, the reported MCID24 − 48m depends on self-reported changes in functional performance (slight improvement – significant deterioration).
3 MCID of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
The MID of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is 24 − 45m, and the reduction of 6MWD by more than 50m within 24 weeks is a negative prognostic factor, which is four times higher than that of patients with a reduction of less than 50m.

4. MCID in patients with pulmonary hypertension
In a study using sildenafil to treat pulmonary hypertension for 12 weeks (Gilbert C, 2009), the minimum change of 6MWD walking distance was taken as the therapeutic index, and the results showed that the average MID of 6MWD was 41m.
summary
6MWT is a reliable, effective and effective measurement method for exercise tolerance of cardiopulmonary patients. The determination of the minimum clinically significant difference (MCID) may vary due to different research methods, disease categories and severity, and other characteristics of the patient population. Multivariate analysis is needed in the future to assess the impact of 6WMT distance change on improvement/deterioration of cue function and accuracy of prognosis.








